We can all hear the ominous music, building slowly, frightfully, until the climax when Jaws attacks! Movies like Jaws have burnt this fearsome group of animals into our psyche, and I think the thought lurks somewhere in our minds whenever we visit the ocean that there are really big fish out there. There are somewhere around 440 species of shark worldwide. They are an ancient group of fish, whose overall lineage dates to before the Age of Dinosaurs. Of these hundreds of species, only 4 are known to have been involved in a significant number of fatal attacks on humans. Worldwide there is an average of 4.3 fatalities per year.
The four most dangerous species have different habits, and therefore the patterns of attacks and their danger to people are different. They are the great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias), oceanic whitetip shark (Carcharhinus longimanus), bull shark (Carcharhinus leucas), and the tiger shark (Galeocerdo cuvier).
The great white, of Jaws fame, is a fearsome predator. Adult sharks are 12-17 feet in length. They are found along both coasts from Mexico into high latitude waters of Alaska, and along the east coast up to Hudson Bay. However, it is also known from deeper ocean waters, and new findings suggest that at least the west coast populations congregate in the open ocean between California and Hawaii for parts of the year. They are predators of marine mammals, turtles, large fish, and even whales. Humans are incidental targets.
- During the hot summer of 1916, the Jersey Shore was the scene of a series of attacks that shuck the public, and was the inspiration for the book Jaws. Between July 1 and July 12, four people were killed. The great white is often blamed, but it could have also been a bull shark. Why there were so many attacks at that time is hard to say, and has not been repeated since.
The oceanic whitetip shark is actually responsible for more fatal attacks on humans than all other species combined, and it does not even frequent the coasts. It is found worldwide, and prefers warm waters and deep ocean areas. It is the unfortunate events of the twentieth century that allowed this shark to become superlative in human fatalities—it is the shark reasonable for attacks on survivors of shipwrecks and downed aircraft. During the war in the Pacific, when ships and planes were regularly shot down, many hundreds of stranded sailors were attacked and killed. Horrific stories from survivors testify to this gruesome bloodshed and led to much research by the Navy in shark repellents. Hopefully, this scale of human carnage will never occur again. And while this species is the most deadly shark, its habits make it of little concern to the average beach-goer.
The tiger shark is found worldwide in mostly equatorial waters. It prefers tropical and sub-tropical warm water, and does not get into the high latitudes like the great white. It tends to stay in deep waters that line reefs, but it does occasionally move into shallow water and channels where it might encounter people. This shark is large, commonly attaining lengths of 10-14 feet, but because of its habits encounters with humans are relatively rare.
In contrast, the bull shark is likely the most dangerous species to humans overall. It too is common in warm waters along coasts, but it also tolerates fresh water, and can migrate into rivers. They have been found far up the Amazon River in South America, and as far north in the Mississippi River as Illinois (yikes!) (Thomerson et al. 1977). These sharks are unpredictable and are often aggressive, and because of their habit of being in shallow waters are probably responsible for the majority of near-shore attacks.
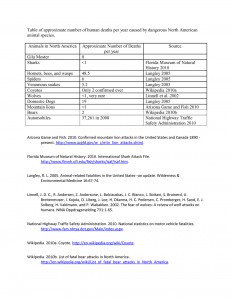
However, having said all of that, the chances of being attacked are very remote. You can see the per year compared with other animals on the chart. Was that deep, ominous music I just heard?
Thomerson, J. E., T. B. Thorson, and R. L. Hempel. 1977. The bull shark, Carcharhinus leucas, from the upper Mississippi River, near Alton, Illinois. Copeia 1977(1):166-168.
Several of the images come from sources recommended in the Nature Wallpaper post.